Laboratories - Spacecraft Research & Design Center
Bifocal Relay Mirror Spacecraft Laboratory

Three Axis Simulator I
Tree Axis Simulator I (TAS I) is our first generation spacecraft simulator utilizing a spherical air-bearing. Three rotational degree-of-freedom with reaction wheels and rate gyros provide ground testing platform of three axis rotational spacecraft.
A simple optical system is also incorporated into the spacecraft simulator to demonstrate the concept of the Bifocal Relay Mirror Spacecraft, which is to relay a laser light from one point to the other distant point. TAS I has also been utilized to demonstrate various spacecraft attitude control and optical beam control methods.
 Three Axis Simulator II
Three Axis Simulator II
Three Axis Simulator II (TAS II) is a second generation spacecraft simulator equipped with more powerful actuators and more accurate sensors. The research goal with TAS II is to demonstrate Acquisition, Tracking, and Pointing (ATP) technologies required by modern spacecraft applications. TAS II is a part of the Bifocal Relay Mirror system, which can simulate the relaying operation of a laser light during orbital motion.
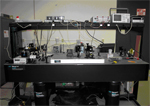 Laser Jitter Control Testbed
Laser Jitter Control Testbed
The Laser Jitter Control Testbed is used for experiments to explore the use of various control techniques to reduce optical jitter induced by mechanical vibration and/or atmospheric turbulence, which degenerates the performance of optical payload systems.
A floating platform (to simulate a spacecraft) houses a shaker to generate vibrational disturbance, a Fast Steering Mirror which is controlled to compensate optical jitter, an accelerometer to measure vibration, and other optical components. An off-board fast steering mirror is also used to corrupt the laser beam and a number of Position Sensing Detectors are used to generate reference signals and error signals.
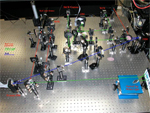 Adaptive Optics Testbed
Adaptive Optics Testbed
The Adaptive Optics Testbed uses adaptive optics to improve the quality of an imaged object.
Light from an object of interest and a red light reference laser beam travel together though the optical components on the table, becoming aberrated in the process.
A Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor samples the wavefront to determine the nature of the aberrations, a computer algorithm computes the phase conjugate correction to compensate for the aberrations, and a deformable mirror is commanded to apply the phase conjugate.
Smart Structure and Attitude Control Laboratory

NPS Space Truss
This testbed is used for structural dynamics and controls research. Providing a scaled laboratory model of the International Space Station structure, the overall dimensions of the NPS Space Truss is 3.76 m long, 0.35 m wide and 0.7 m tall. Two piezoceramic struts are installed as actuators near the base of the truss.
The output force for the actuator is 0-100 N and the displacement range is 0-90 µm. A linear proof mass actuator, located at one end of the truss, can be used to generate structural disturbances.

Precision Pointing Hexapod
The Positioning Hexapod is used to research control algorithms for vibration isolation of an imaging payload and fine steering of the payload boresight. Six electromagnetic voice coil actuators employ in-line accelerometers for control of high frequency vibrations.
Lower frequency boresight steering and vibration isolation is achieved using a laser photo-diode 2-axis position detector and eddy current position sensors. The system can deliver over 5.7 mm of axial travel, 20 mm of lateral motion, 2.5 degrees of platform tilt and 10 degrees of platform rotation.

Flexible Spacecraft Simulator (FSS)
Flexible Spacecraft Simulator (FSS) simulates a single axis rotational spacecraft with
flexible space structures.
FSS utilizes planar air-pads to create frictionless rotational motion. FSS has been successfully used to demonstrate various control techniques for large slew maneuvers.
FLTSATCOM Laboratory

FLTSATCOM Laboratory
This laboratory hosts a ground validation model of the Navy communications satellite, FLTSATCOM, and the ground support equipment allowing communication with, and operation of the satellite.
NPS developed the FLTSATCOM Attitude Control Simulator, which provides a graphical display of the spacecraft’s attitude and rotational motion in response to commands similar to the commands required for flight model FLTSATCOM spacecraft.
Spacecraft Design Laboratory

Spacecraft Design Laboratory
This laboratory provides a dedicated facility for collaborative for space system design and hosts modern engineering tools and a library of related technical materials. The lab is modeled after the Concept Design Center (CDC) operated by The Aerospace Corporation.
The engineering design tools include GENSAT, a general-purpose software application for satellite design, multiple software packages for mission cost estimation, Satellite Toolkit (STK), NASTRAN, IDEAS, and Matlab/Simulink.
Adaptive Optics Beam Control Laboratory

Adaptive Optics Beam Control Laboratory
New laboratory provides clean room envrironment (Class 10,000) for optical elements. The lab facilitates beam control testbed for high energy laser systems with research topics on adaptive optics, jitter control, structure and optics optimization, and testbed development.

HEL Beam Control Testbed
The purpose of the testbed is to develop beam control technologies for High Energy Laser (HEL) systems. The area of research includes optical jitter control; wavefront sensing and correction techniques; mirror alignment and shape control; and acquisition, tracking, and pointing using adaptive and robust control techniques.

HEL Beam Control Testbed
The purpose of the testbed is to develop beam control technologies for High Energy Laser (HEL) systems. The area of research includes optical jitter control; wavefront sensing and correction techniques; mirror alignment and shape control; and acquisition, tracking, and pointing using adaptive and robust control techniques.

